Dubbo的SPI在Dubbo源码里很经常看到,是Dubbo扩展点的一种实现方式。Dubbo的SPI机制有点类似于Java的SPI机制,这里就不介绍Java的SPI机制了。
示例
我们先来看看如下比较简单的服务发布的配置文件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<dubbo:application name="foo-provider" owner="bar"/>
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181" simplified="true"/>
<dubbo:protocol name="hessian" port="20880"/>
<dubbo:service interface="com.example.FooService" ref="foo" protocol="hessian" />
<bean name="foo" class="com.example.FooServiceImpl"/>
</beans>
我们可以看到这里protocol填写hessian,那么rpc调用就采用hessian的方式调用。如果不写的话,就会采用dubbo的protocol调用。那么dubbo是怎么做到这样动态的切换protocol呢?下面我们来探探究竟。
分析
dubbo-rpc-hessian目录结构
我们可以在dubbo的源码工程下dubbo-rpc子项目下找到dubbo-rpc-hessian,我们看到里面的目录结构如下:
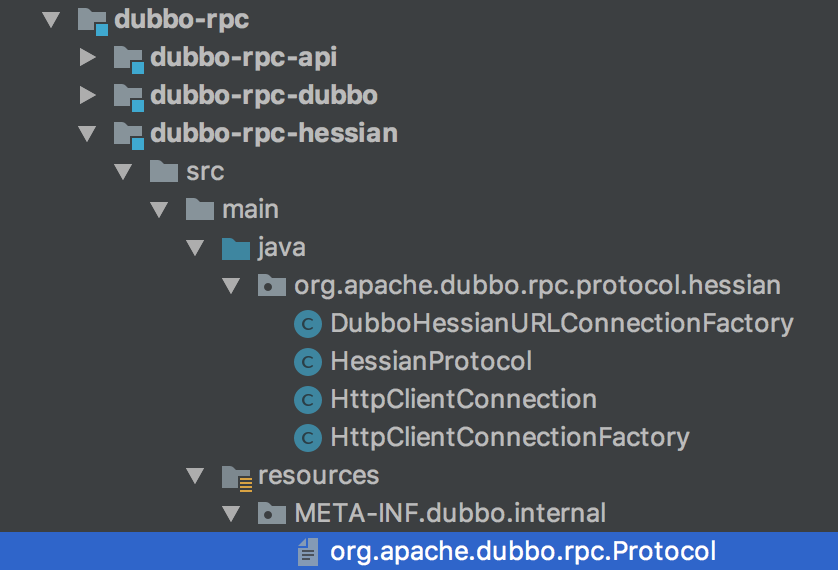
首先这里面有个HessianProtocol是实现了Protocol接口的,其次在resource目录下有META-INF/dubbo/internal这样的目录,而这个目录有个带有Protocol类全路径的org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol文件,文件内容是hessian=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.hessian.HessianProtocol,这让我们想到了和Java的SPI有点类似了。顺着这个目录在dubbo源码工程里搜,会发现是在ExtensionLoader里会这个目录进行加载。
SPI的加载路径
- /META-INF/dubbo/internal
- /META-INF/dubbo
- /META-INF/services
SPI的类目录结构
我们可以在dubbo的源码工程下dubbo-common子项目下找到extension目录和dubbo-config子项目下dubbo-config-spring项目的extension目录,如下图:
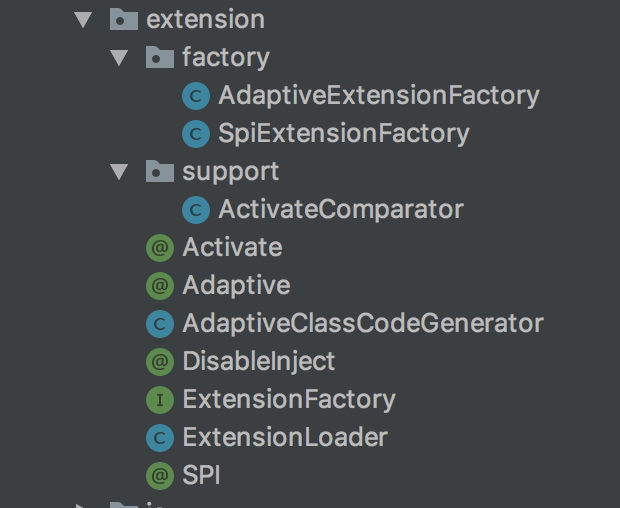
ExtensionLoader
我们在ExtensionLoader中看到一个比较重要的方法getAdaptiveExtension,我们先用一张时序图来了解一下这个方法
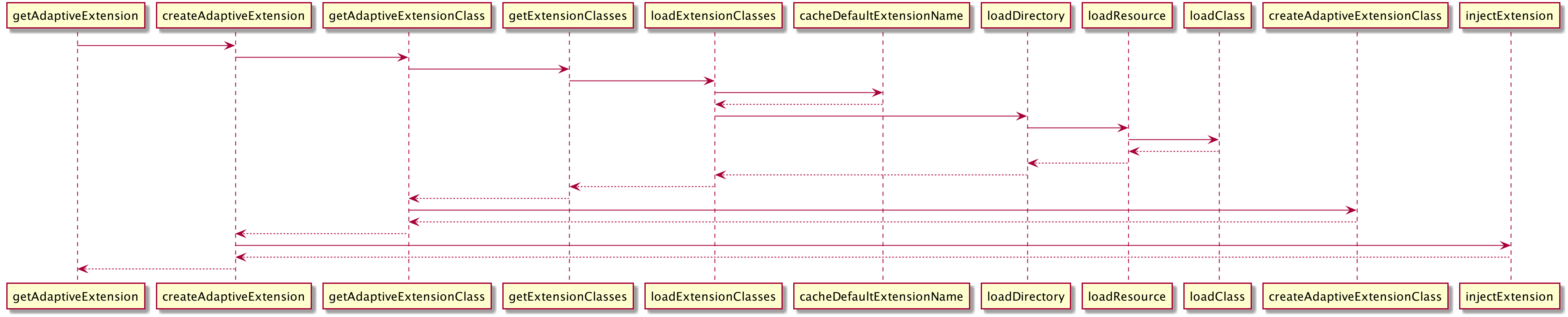
我们来看下ExtensionLoader#cacheDefaultExtensionName方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
private void cacheDefaultExtensionName() {
final SPI defaultAnnotation = type.getAnnotation(SPI.class);
if (defaultAnnotation != null) {
String value = defaultAnnotation.value();
if ((value = value.trim()).length() > 0) {
String[] names = NAME_SEPARATOR.split(value);
if (names.length > 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("More than 1 default extension name on extension " + type.getName()
+ ": " + Arrays.toString(names));
}
if (names.length == 1) {
cachedDefaultName = names[0];
}
}
}
}
这个方法主要的用途是:先判断接口类是否@SPI注解,如果有@SPI注解,且value有值,则设置为cachedDefaultName,这个cachedDefaultName为后续createAdaptiveExtensionClass创建动态代理类所用。
再来看下一个重要的方法ExtensionLoader#loadClass
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
private void loadClass(Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses, java.net.URL resourceURL, Class<?> clazz, String name) throws NoSuchMethodException {
if (!type.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Error occurred when loading extension class (interface: " +
type + ", class line: " + clazz.getName() + "), class "
+ clazz.getName() + " is not subtype of interface.");
}
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Adaptive.class)) {
cacheAdaptiveClass(clazz);
} else if (isWrapperClass(clazz)) {
cacheWrapperClass(clazz);
} else {
clazz.getConstructor();
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(name)) {
//若有@Extension类注解,则取@Extension的value值,否则取接口的前缀的小写(如HessianProtocol就是hessian)。
name = findAnnotationName(clazz);
if (name.length() == 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No such extension name for the class " + clazz.getName() + " in the config " + resourceURL);
}
}
String[] names = NAME_SEPARATOR.split(name);
if (ArrayUtils.isNotEmpty(names)) {
cacheActivateClass(clazz, names[0]);
for (String n : names) {
cacheName(clazz, n);
saveInExtensionClass(extensionClasses, clazz, name);
}
}
}
}
这个方法会找到所有实现类,如果某个实现类带有@Adaptive,会标记这个实现类为指定的适配类,直接返回。如果实现类不是一个装饰者,则保存在扩展类中。
接下来还有个重要的方法ExtensionLoader#createAdaptiveExtensionClass
1
2
3
4
5
6
private Class<?> createAdaptiveExtensionClass() {
String code = new AdaptiveClassCodeGenerator(type, cachedDefaultName).generate();
ClassLoader classLoader = findClassLoader();
org.apache.dubbo.common.compiler.Compiler compiler = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(org.apache.dubbo.common.compiler.Compiler.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
return compiler.compile(code, classLoader);
}
动态生成代理类代码,并且动态编译进去,我们来看看Protocol接口动态生成的自适应类长什么样。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
package org.apache.dubbo.rpc;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionLoader;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Exporter;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.RpcException;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.URL;
public class Protocol$Adaptive implements Protocol {
public void destroy() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("The method public abstract void org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.destroy() of interface org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol is not adaptive method!");
}
public int getDefaultPort() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("The method public abstract int org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.getDefaultPort() of interface org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol is not adaptive method!");
}
public Exporter export(Invoker arg0) throws RpcException {
if (arg0 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument == null");
if (arg0.getUrl() == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument getUrl() == null");
URL url = arg0.getUrl();
String extName = (url.getProtocol() == null ? "dubbo" : url.getProtocol());
if (extName == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to get extension (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol) name from url (" + url.toString() + ") use keys([protocol])");
//生成指定协议的扩展点
Protocol extension = (Protocol) ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getExtension(extName);
return extension.export(arg0);
}
public org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker refer(java.lang.Class arg0, org.apache.dubbo.common.URL arg1) throws org.apache.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg1 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
org.apache.dubbo.common.URL url = arg1;
String extName = (url.getProtocol() == null ? "dubbo" : url.getProtocol());
if (extName == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to get extension (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol) name from url (" + url.toString() + ") use keys([protocol])");
//生成指定协议的扩展点
//当extName为dubbo时,则extension为ProtocolListenerWrapper(ProtocolFilterWrapper(QosProtocolWrapper(DubboProtocol)))这样的装饰器
Protocol extension = (Protocol) ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getExtension(extName);
return extension.refer(arg0, arg1);
}
}
总结
Dubbo SPI机制,会加载META-INF/dubbo/internal, META-INF/dubbo, META-INF/services里带有接口的完整路径的文件,文件内容的格式是{key}={value}。其中如果不加{key}=,dubbo会默认给你个key,key的规则是接口类的前缀全小写(如ConsumerContextFilter的key就是consumercontext;value是实现类的全路径。若想指定一个自适应扩展点,则需在实现类加上@Adaptive类级别注解,否则动态生成一个{Interface}$Adaptive类。
